The Importance of Air Control Valves
The Importance of Air Control Valves
3. Air-to-Air Heat Exchangers Used predominantly in ventilation systems, these heat exchangers transfer heat between two air streams without mixing them. This type is crucial for reducing heating and cooling demands in buildings, thus contributing to energy savings.

2. Compression Units Compressors play a critical role in moving gas through the pipelines. These machines increase the pressure of the gas, enabling it to flow efficiently over long distances. Some distribution stations may also contain additional compressors to maintain pressure levels as the gas is distributed.
In various industrial applications, the management of gas pressure is crucial for maintaining safety and operational efficiency. One critical component in achieving this is the gas safety relief valve. This device plays an essential role in preventing overpressure situations that could lead to catastrophic failures or hazardous incidents. Understanding its function, importance, and maintenance is vital for anyone involved in industries that utilize gases.
How Pressure Reducing Valves Work
4. Rebalancing Periodically, the basket may need to be rebalanced to reflect changes in market conditions or asset performance. Rebalancing helps to maintain the desired risk level and ensure alignment with investment goals.
Gas pressure reduction stations also help to optimize the performance of natural gas distribution systems. By reducing the pressure of the gas at strategic points along the pipeline, these stations help to maintain the flow of gas at a steady rate. This ensures that gas is delivered to end-users in a timely and efficient manner, without causing disruptions or pressure fluctuations.
 These regulators are designed to handle high-pressure environments and withstand the rigors of industrial operations These regulators are designed to handle high-pressure environments and withstand the rigors of industrial operations
These regulators are designed to handle high-pressure environments and withstand the rigors of industrial operations These regulators are designed to handle high-pressure environments and withstand the rigors of industrial operations gas pressure regulator. They are often equipped with additional features such as pressure gauges, shut-off valves, and relief valves for added safety and functionality.
gas pressure regulator. They are often equipped with additional features such as pressure gauges, shut-off valves, and relief valves for added safety and functionality.
Pneumatic control valves come in various types, each designed for specific applications. Ball valves, butterfly valves, and solenoid valves are prevalent in pneumatic systems. Ball valves provide quick shut-off capabilities, while butterfly valves offer a more compact and lightweight solution for regulating flow. Solenoid valves, on the other hand, use electromagnetic coils to control flow, allowing for precise on-off switching in applications where automated control is required.
1. Enhanced Gas Quality One of the primary benefits of using gas coalescer filters is the improvement in gas quality. By efficiently removing water and contaminants, these filters help prevent corrosion in pipelines, reduce the risk of hydrate formation, and ensure that the gas meets the quality specifications mandated by regulatory bodies.
Functions of a Filter Separator
In the oil and gas industry, maintaining the quality and integrity of extracted products is paramount. One of the essential components in achieving this is the use of filter separators. These devices play a pivotal role in separating different phases of produced fluids while removing impurities. In this article, we will delve into the function, design, and significance of filter separators in ensuring efficient operations.
The Rise of Liquefied Natural Gas (LNG)
Conclusion
Gas regulators can be classified into several categories based on their intended application
Despite its potential, gasification also faces challenges. High capital costs, feedstock variability, and the need for sophisticated technology can hinder widespread adoption. However, ongoing research and development efforts aim to address these issues, making gasification a more viable option for large-scale energy production.
2. Efficiency Gas pressure reduction stations play an essential role in maintaining the efficiency of the gas distribution network. By managing pressure levels effectively, they ensure that gas can flow smoothly into distribution networks without causing strain on pipelines. This efficiency lowers operational costs and helps prevent gas loss due to leaks.

1. Pressure Sensing The diaphragm or piston responds to changes in pressure. When the inlet gas pressure rises above the desired level, the diaphragm moves against the spring, causing the valve to close partially. Conversely, if the pressure drops below the set point, the diaphragm moves down, allowing more gas to flow through and increasing the outlet pressure.
Gas safety valves are critical components in various industrial applications, ensuring the safe handling and usage of gas. These valves play an essential role in maintaining pressure control, preventing accidents, and protecting equipment from potential failures. As industries increasingly rely on gas for energy production, heating, and manufacturing processes, understanding the significance and functionality of gas safety valves becomes paramount.
Safety and Efficiency
3. High-Pressure Reducers Designed for high-pressure systems, they are built to withstand extreme conditions while steadily regulating pressure.


Environmental Benefits
How Pressure Reducing Regulators Work

How Gas Safety Valves Work
In an increasingly fast-paced world, our daily lives are filled with stress and pressure, both physical and emotional. Therefore, the significance of pressure relief devices, particularly those designed for healthcare and personal well-being, cannot be underestimated. The term مزلقة تخفيف الضغط, or pressure relief device, encompasses a variety of tools and techniques aimed at alleviating pressure and minimizing discomfort in various settings, whether in hospitals, homes, or workplaces.
The development of supercharging began with pioneers like Tesla, which launched its Supercharger network in 2012. Designed to support long-distance travel, Tesla’s Superchargers provide high voltage direct current (DC) charging, significantly reducing the time it takes to recharge a battery compared to traditional alternating current (AC) chargers. Consequently, Tesla’s Supercharger network has become one of the largest and most recognizable in the world, featuring thousands of stations across multiple continents.

- Energy Efficiency Modern electric valves are designed to minimize energy consumption, contributing to overall system efficiency.
Pressure regulators work by using a diaphragm or a spring-loaded mechanism to balance the incoming gas pressure with a preset outlet pressure. As the gas flows through the regulator, the diaphragm or spring adjusts to maintain a consistent pressure, even when fluctuations occur in the supply line. This ensures that appliances receive a steady and reliable supply of gas, preventing the risk of damage or malfunction due to high or low pressures.

3. Longevity of Equipment Consistent pressure reduces wear and tear on machinery, extending its lifespan and minimizing downtime associated with maintenance and repairs.
The operation of a filter separator begins with the inflow of natural gas. As the gas enters the unit, it typically encounters a filtering medium, which traps solid particulates. This is followed by the separation phase, where the gas is directed into a separation chamber. In this chamber, gravity plays a vital role. The heavier liquid contaminants, such as water and hydrocarbons, settle at the bottom while the cleaner gas rises to the top.
3. Ambulatory Blood Pressure Monitors These sophisticated devices are worn by the patient for 24 hours, measuring blood pressure at regular intervals throughout the day and night. This provides a comprehensive view of blood pressure patterns and helps identify white coat syndrome, where patients experience elevated readings in clinical settings due to anxiety.
- Coalescing Filters These specialized filters are designed to remove very fine water droplets from the gas stream by allowing them to coalesce into larger droplets that can be separated more efficiently.
Gas Distribution Stations Essential Hubs in Energy Supply
At the heart of smart regulation is the use of big data and analytics. Traditional regulatory approaches often rely on static rules and manual oversight, which can lead to inefficiencies and slow responses to emerging challenges. In contrast, smart regulators harness data from multiple sources—ranging from social media to IoT devices—to gain real-time insights into activities within their jurisdictions. This data-driven approach allows regulators to identify trends, anticipate issues before they escalate, and implement timely interventions.
 Its small size, however, does not compromise on strength or performance, making it a popular choice in various industries Its small size, however, does not compromise on strength or performance, making it a popular choice in various industries
Its small size, however, does not compromise on strength or performance, making it a popular choice in various industries Its small size, however, does not compromise on strength or performance, making it a popular choice in various industries bearing 32006x.
bearing 32006x.

 It emphasizes the importance of proper handling and lubrication to maximize bearing performance and longevity It emphasizes the importance of proper handling and lubrication to maximize bearing performance and longevity
It emphasizes the importance of proper handling and lubrication to maximize bearing performance and longevity It emphasizes the importance of proper handling and lubrication to maximize bearing performance and longevity timken deep groove ball bearing catalog. Furthermore, it provides guidance on how to interpret bearing failure patterns, helping users prevent potential issues before they arise.
timken deep groove ball bearing catalog. Furthermore, it provides guidance on how to interpret bearing failure patterns, helping users prevent potential issues before they arise.
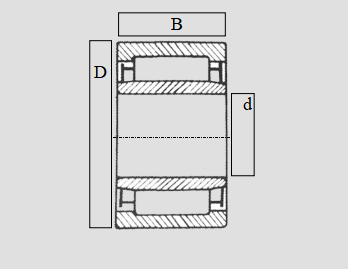
 6310 2rs bearing.
6310 2rs bearing.